Cover Your Bases Across Regulatory Compliance, Insurance and Privacy Training
Over the past few years, ransomware attacks have significantly impacted critical infrastructure and supply chains, resulting in millions of dollars in losses.
These cyber events have reached such a scale and severity that even the White House has urged businesses to step up their security measures. In September 2022, President Biden issued a proclamation officially designating October as Cybersecurity Awareness Month in the administration's continued bid to improve the nation’s cyber security.
This article outlines common exposures companies face as well as a checklist of privacy and compliance requirements and training, insurance coverages, and risk mitigation resources businesses can implement to protect themselves before a cyber event happens.
Common Cyber Security and Privacy Compliance Exposures
For businesses large and small, compliance with federal, state and foreign privacy laws and regulations has become an essential obligation. These laws govern a company’s collection, storage, use, sharing and disposal of personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI) and payment card information (PCI). A company’s inadvertent failure to abide by these laws, or its failure to timely and fully disclose how it performs such tasks, can make it a target for regulatory proceedings and civil class actions. These lapses can also be a source of reputational damage.
Employment and consumer-related risks and exposures also have become more prevalent, particularly under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). An organization’s web presence needs to be accessible to all, including those with disabilities.
Failure to protect private information can also lead to consumer class actions. And, organizations could be presented with shareholder suits if the value of an organization is harmed due to a cybersecurity event.
These stats put into perspective just how devastating a breach can be on a business.
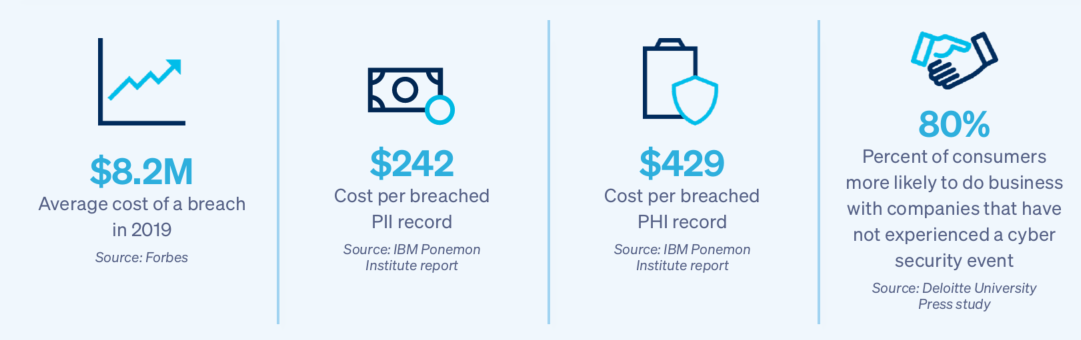
In short, the risks are real, particularly for small and medium-sized firms which typically do not have the robust cybersecurity protections of larger companies.
What Can You Do to Help Protect Your Client’s Business?
Use this checklist to ensure adequate risk mitigation and protection for businesses of all sizes.
1. Don’t ignore data security and privacy compliance.
While the requirements for each business will be different, there are some general practices to follow:
- Create and memorialize regulatory compliance policies and procedures
- Provide compliance training to key personnel
- Inventory and assess the PII, PHI and PCI collected so that you have a record of what is in your possession
- Update your website home page to comply with applicable laws
- Address non-discrimination issues to provide consumers with the right to equitable service and pricing
- Implement and regularly update appropriate incident response and business continuity plans
- Obtain social engineering training from a qualified vendor
- Use multifactor authentication for everyone with remote access to your systems as well as when sending funds to third parties
- Conduct an audit of (or obtain an assessment certification from) your vendors and others with access to your electronic infrastructure to ensure these third parties are compliant with governing law and have cybersecurity protections at least as robust as yours
2. Purchase a broad cyber liability insurance policy.
Work closely with your wholesale insurance broker to evaluate the coverage your client currently has, what they need based on their business’s unique risk factors, and the insurance coverages that they’re contemplating buying or not buying. Key coverages include:
- Security & privacy liability addressing PII, PHI and PCI
- Regulatory coverage including fines and penalty coverage
- First-party breach costs and response coverage
- Social engineering coverage
- Ransomware coverage
- Cyber business interruption coverage
- Data restoration coverage
- Reputational harm coverage
3. Take advantage of additional loss mitigation services provided alongside the cyber liability insurance policy.
These services can include:
- Network vulnerability scans
- Ongoing updates on vulnerabilities and patches specific to your own security posture
- Social engineering training for employees
- Tabletop exercises to prepare for a breach event
- Breach coaches
- Information security hotlines
- Training videos
Summary
In today’s world, risk transfer alone isn’t enough to protect a business from the implications of a cyberattack. The right combination of a well-placed cyber liability insurance policy, compliance knowledge and review, employee training, and loss mitigation services are an effective approach to reduce a company’s cyber risks and potential exposures.